खनन और खनिज उद्योगों में पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता विषय पर विशेषज्ञों का मंथन पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता मानव समाज के निरन्तर अस्तित्व, समृद्धि और स्वास्थ्य के लिए मूलभूत शर्त है। हमारी न्यू जनरेशन को स्पीड और टेक्नोलॉजी पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना होगा ताकि भविष्य को सुनहरा बनाया जा सके। उक्त विचार मुख्य अतिथि श्री एमपी सिंह, प्रधान मुख्य अभियंता, केंद्रीय विद्युत प्राधिकरण विद्युत मंत्रालय भारत सरकार, नई दिल्ली ने व्यक्त किए श्री सिंह भूपाल नोबल्स स्नातकोत्तर महाविद्यालय में भूविज्ञान विभाग द्वारा "खनन और खनिज उद्योगों में पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता" विषय पर आयोजित दो दिवसीय राष्ट्रीय कॉन्फ्रेंस के समापन पर बोल रहे थे। दो दिवसीय राष्ट्रीय कान्फ्रेंस का भव्य समापन सम्मानित अतिथि प्रो विनोद अग्रवाल सदस्य, भारत सरकार नई दिल्ली स्थित MOEFCC की विशेषज्ञ मूल्यांकन समिति, (सि एण्ड टीपी) अपने उद्बोधन में कहा कि पर्यावरण स्थिरता सरकार और समाज दोनों की जिम्मेदारी है। वर्तमान में खनन उद्योग विभिन्न प्रावधानों एवं कानूनों के तहत कार्य कर रहा है ताकि पर्यावरण को सुरक्षित रखा जा सके। आयोजन सचिव डॉ. हेमंत सेन न...
Dulong and Petit's law
- According to Dulong and Petit's law the product of atomic weight and specific heat for all the elements in its solid state is always constant and its value is approximately 6.4.
- This law is used to determine the atomic weight of substance.
Dulong and Petit’s law from Kinetic theory
- According to the law of equi-partition of energy, the average kinetic energy of translation associated with each degree of freedom is 1/2kT.
- If the oscillatory motion of atom is simple harmonic then in each oscillation the average kinetic energy = Average potential energy.
= 1/2 kT + 1/2 kT = kT
Since there are three degrees of freedom for oscillatory motion of each atom
Since there are three degrees of freedom for oscillatory motion of each atom
So the total energy of each atom = 3kT
If we consider the 1 gm-atom of any solid at absolute temperature T
So the number of atoms in 1 gm-atom of gas = N, where N is Avogadro number
Total energy of 1 gm of solid
U = N * 3 kT = 3NkT [ R = Nk ]
U = 3RT
dU/dT = 3R
Since dU/dT is the atomic heat of solid at constant volume i.e., Cv
So, Cv = 3R
Since R = 1.98 cal/gm-atom/°C
So, Cv = 3 * 1.98 = 5.94 cal/gm-atom/°C
Atomic heat of solid = 6 cal cal/gm-atom/°C (approximate)
Thus it agrees with Dulong and Petit's law
Failure of Dulong and Petit's law
- C, B, Si like non-metallic elements have value of atomic heat different from 6.4 at normal temperature (about 6.0).
- But above 500°C their value tends to about 6.4.
- At absolute zero temperature the value of atomic heat of all the elements tends to zero.
It is clear from the following figure
Explanation of Failure of Dulong and Petit's law
To know about this lecture in more detail please visit on https://youtu.be/R_xEBgzUmkQ



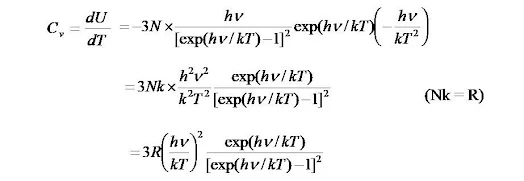

Comments
Post a Comment