खनन और खनिज उद्योगों में पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता विषय पर विशेषज्ञों का मंथन पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता मानव समाज के निरन्तर अस्तित्व, समृद्धि और स्वास्थ्य के लिए मूलभूत शर्त है। हमारी न्यू जनरेशन को स्पीड और टेक्नोलॉजी पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना होगा ताकि भविष्य को सुनहरा बनाया जा सके। उक्त विचार मुख्य अतिथि श्री एमपी सिंह, प्रधान मुख्य अभियंता, केंद्रीय विद्युत प्राधिकरण विद्युत मंत्रालय भारत सरकार, नई दिल्ली ने व्यक्त किए श्री सिंह भूपाल नोबल्स स्नातकोत्तर महाविद्यालय में भूविज्ञान विभाग द्वारा "खनन और खनिज उद्योगों में पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता" विषय पर आयोजित दो दिवसीय राष्ट्रीय कॉन्फ्रेंस के समापन पर बोल रहे थे। दो दिवसीय राष्ट्रीय कान्फ्रेंस का भव्य समापन सम्मानित अतिथि प्रो विनोद अग्रवाल सदस्य, भारत सरकार नई दिल्ली स्थित MOEFCC की विशेषज्ञ मूल्यांकन समिति, (सि एण्ड टीपी) अपने उद्बोधन में कहा कि पर्यावरण स्थिरता सरकार और समाज दोनों की जिम्मेदारी है। वर्तमान में खनन उद्योग विभिन्न प्रावधानों एवं कानूनों के तहत कार्य कर रहा है ताकि पर्यावरण को सुरक्षित रखा जा सके। आयोजन सचिव डॉ. हेमंत सेन न...
Phase velocity and Group velocity
Phase velocity (Wave velocity)
- If a single monochromatic wave (wave of single frequency or wavelength) travels through a medium, then the velocity through which it propagate is wave velocity.
- Equation of plane progressive wave propagating in x-direction
- Here a = amplitude, ω = angular frequency, and k = 2π / λ = wave vector or propagation constant
- Since in wave motion, the particles of the medium vibrates about their mean position continuously, the velocity acquired by particle during this motion is particle velocity.
- During this motion, the disturbance (crest or trough) also produced and they also move in the direction in which the wave propagate and also with the same velocity.
- The velocity of the disturbance through which it advances through the medium is phase velocity (wave velocity).

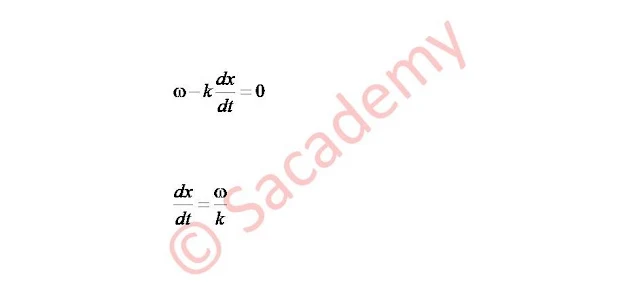
- Above equation gives the wave velocity.
- Thus the ratio of angular frequency to the propagation constant (wave vector) is known as wave velocity.
- In equation y = a sin (ωt - kx), (ωt - kx) is phase of wave motion
- For the planes of constant phase or wavefronts
- Above expression represents the wave velocity.
- Since the wave velocity is the velocity with which planes of constant phase advance through the medium, and above expression is obtained for such type of wave, so it is also known as phase velocity.
Group velocity
- In practical life we come across pulse or group of wave of slightly different frequencies. This group of waves are wave packets.
- A wave packet refers to the case where two or more waves exist simultaneously.
- The group velocity of a wave packet is the velocity with which the maximum amplitudes of the group advances in the medium.
- This is the velocity with which the energy in the group is transmitted.
- The group velocity is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity with respect to wave vector.
- Let a wave packet is made up of two harmonic waves

- Let on superposition, these waves form a wave packet, then resultant displacement of wave packet

- The amplitude of this equation is modulated by


- Here figure (a) and (b) shows the two waves of slightly different frequencies, and figure (c) shows the resultant wave of these two waves.

- If △ω and △k are very small.

- To know more about phase velocity and group velocity please click on the link https://youtu.be/as-a0sUw1RQ or for bilingual (Hindi/English) https://youtu.be/sLhr0cJWAew

Comments
Post a Comment