खनन और खनिज उद्योगों में पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता विषय पर विशेषज्ञों का मंथन पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता मानव समाज के निरन्तर अस्तित्व, समृद्धि और स्वास्थ्य के लिए मूलभूत शर्त है। हमारी न्यू जनरेशन को स्पीड और टेक्नोलॉजी पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना होगा ताकि भविष्य को सुनहरा बनाया जा सके। उक्त विचार मुख्य अतिथि श्री एमपी सिंह, प्रधान मुख्य अभियंता, केंद्रीय विद्युत प्राधिकरण विद्युत मंत्रालय भारत सरकार, नई दिल्ली ने व्यक्त किए श्री सिंह भूपाल नोबल्स स्नातकोत्तर महाविद्यालय में भूविज्ञान विभाग द्वारा "खनन और खनिज उद्योगों में पर्यावरणीय स्थिरता" विषय पर आयोजित दो दिवसीय राष्ट्रीय कॉन्फ्रेंस के समापन पर बोल रहे थे। दो दिवसीय राष्ट्रीय कान्फ्रेंस का भव्य समापन सम्मानित अतिथि प्रो विनोद अग्रवाल सदस्य, भारत सरकार नई दिल्ली स्थित MOEFCC की विशेषज्ञ मूल्यांकन समिति, (सि एण्ड टीपी) अपने उद्बोधन में कहा कि पर्यावरण स्थिरता सरकार और समाज दोनों की जिम्मेदारी है। वर्तमान में खनन उद्योग विभिन्न प्रावधानों एवं कानूनों के तहत कार्य कर रहा है ताकि पर्यावरण को सुरक्षित रखा जा सके। आयोजन सचिव डॉ. हेमंत सेन न...
Grand canonical ensemble
Grand canonical ensemble
- Microcanonical ensemble is a collection of independent assemblies in which energy (E), volume (V), and number of particles (N) remain constant.
- Canonical ensemble is a collection of independent assemblies in which temperature (T), volume (V), and number of particles (N) remain constant.
- It mean a microcanonical ensemble ⟶ Canonical ensemble, if we ignore the condition E = constant.
- Therefore the energy exchange takes place in this ensemble.
- Actually in chemical process, the number of particles N varies and it is very difficult to keep the number of particles constant in various phenomenon like radioactive decay process.
- Thus grand canonical ensemble is an ensemble in which the exchange of energy as well as the number of particles takes place with the heat reservoir.
- The grand canonical ensemble is a collection of essentially independent assemblies having the same temperature T, volume V, and a chemical potential µ.

- Thus grand canonical ensemble is a situation in which we know both the average energy and the average number of particles in assembly, otherwise we don’t know the state of the system.
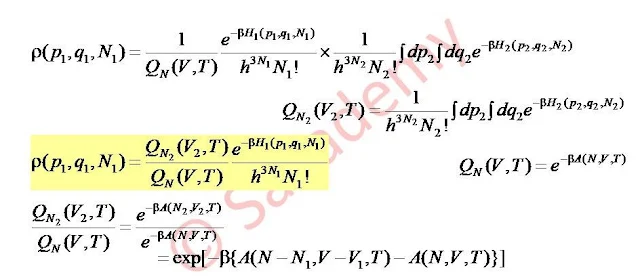
- The density function in Гspace for grand canonical ensemble = ρ (p, q, N)
- Here p is momenta, q is coordinate and N is number of particles.
- To find ρ (p, q, N), we consider the canonical ensemble for a system with particles N, volume V and temperature T.
- Here we can not take exactly V = constant, so our focus is on a small sub-volume V1 of the system.
- Let N1 particles be in volume V1, and N2 particles be in volume V2
- N1 + N2 = N ⇒ N2 = N - N1 and V1 + V2 = V ⇒ V2 = V - V1
- Also we assume that V2 >> V1 and N2 >> N1
- If H1 and H2 be the Hamiltonian of the system then
- The total Hamiltonian of the composite system
- H (p, q, N) = H1 (p1, q1, N1) + H2 (p2, q2, N2)
Partition function of the system
- The partition function of the total system

- In the last term we consider that the system under consideration to become infinite in size or 0 ≤ N < ∞.
- For thermodynamic function, we define grand partition function

Average number of particle
- By ensemble average, the average number of particles





Comments
Post a Comment